A sampling of recent articles, videos, and images related to human expansion into the solar system (see also previous space settlement postings):
** Map shows Mars settlers where to find water: NASA’s Treasure Map for Water Ice on Mars | NASA

Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU”
A new paper published in Geophysical Research Letters will help [select landing spots on Mars] by providing a map of water ice believed to be as little as an inch (2.5 centimeters) below the surface.
Water ice will be a key consideration for any potential landing site. With little room to spare aboard a spacecraft, any human missions to Mars will have to harvest what’s already available for drinking water and making rocket fuel.
NASA calls this concept “in situ resource utilization,” and it’s an important factor in selecting human landing sites on Mars. Satellites orbiting Mars are essential in helping scientists determine the best places for building the first Martian research station. The authors of the new paper make use of data from two of those spacecraft, NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and Mars Odyssey orbiter, to locate water ice that could potentially be within reach of astronauts on the Red Planet.
“You wouldn’t need a backhoe to dig up this ice. You could use a shovel,” said the paper’s lead author, Sylvain Piqueux of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. “We’re continuing to collect data on buried ice on Mars, zeroing in on the best places for astronauts to land.”
See also:
- For Mars colonization, new water map may hold key of where to land – NASASpaceFlight.com
- A new map of the water ice on Mars | Behind The Black
** Recent interviews on The Space Show dealing with space settlement:
**** Fri, 12/13/2019 – Morgan Irons discussed “space farming and agriculture, closed and quasi-closed loop life support, food security and lots more”.
**** Thu, 12/05/2019 – Al Globus discussed”new information and an implementation program for his ELEO space habitat” concepts.
**** Tue, 12/03/2019 – Bryce Meyer discussed “space farms, growing food in space, lunar agriculture, food on Mars, recycling human waste, space farm energy needs and TRL’s”.
** A discussion of the definition of space settlement by Dale A. Skran: SPACE BASICS: What is Space Settlement? – National Space Society
Before we get too far into this, it is important to clearly differentiate between “space settlement” and “a space settlement.” Space settlement is the general process of developing and settling space. A space settlement is a specific place in space where people live, work, and raise families.
Let’s start with a relevant dictionary definition of settlement—“the settling of persons in a new place.” This definition is almost immediately self-referential, as it refers to “settling of persons.” When we look at “settle” the verb, we see definitions that include “to migrate to and organize (an area, territory, etc); colonize,” “to cause to take up residence,” and “to furnish (a place) with inhabitants or settlers.”
All these definitions revolve around people living in a new place—“colonizing,” “taking up residence,” etc. This is very important—“taking up residence” implies permanence, family life, a job, and so on. A soldier being assigned to a base for a year is not “colonizing” or “taking up residence”—instead they are “being deployed.” A scientist might be “assigned” to work at a base in Antarctica for a period of time, but they are not “colonizing” Antarctica.
Thus, I propose that a “space settlement” is a group of people (men, women, children) who move to some specific location in space (Moon, Mars, an asteroid, orbital free space, etc.) to take up permanent residence there. This implies that they will raise their children in this “space settlement,” work in or near the “space settlement,” and in all probability die and have their remains disposed of there as well.
Skan concludes with
To summarize, the space settlements we are working to establish have the following characteristics:
-
- Families live in them on a permanent basis
- The settlements engage in commercial activity that generates the wealth needed to sustain them, and are not dependant on infusions of government funds.
- They are large enough and diverse enough to be, at least potentially, both economically and biologically self-sustaining.
- They may have a variety of organizational forms, including kibbutz style common ownership of the settlement, systems based on private property, company towns, or religious communities.
** OffWorld is developing universal industrial robots for “heavy lifting” on Earth, Moon, asteroids and Mars: Meet OffWorld, the startup that wants to mine the moon with a swarm of robots | Digital Trends
To say that OffWorld’s dream is an ambitious one is to put it mildly. The company envisions a future in which millions of smart robots work together using swarm intelligence “on and offworld” to build the infrastructure of tomorrow. Long term, they even imagine the possibility of using the robots to mine for materials which could be used to build new chips “with zero reliance on terrestrial supply.”
https://vimeo.com/223289927
Check out OffWorld’s Master Plan (pdf).
** Baking cookies and other tasty foods in space: Time Dodd, the Everyday Astronaut, reports on the new baking system on the ISS: How NASA will bake in space for the first time and why that’s a BIG deal! – Everyday Astronaut
More at DoubleTree Cookies in Space – The First Food Ever Baked in Space
** A video of “Olympus”, Bigelow’s largest expandable habitat design:
Featuring a simple cut-away view of the B2100 “Olympus” to show the interior, this video is a compilation of previously uploaded Bigelow habitat clips as well as some new ones. Enjoy!
B330 and B2100 models by fragomatik.
ISS model by NASA, adapted for use within IMAGINE v2.19 by fragomatik.
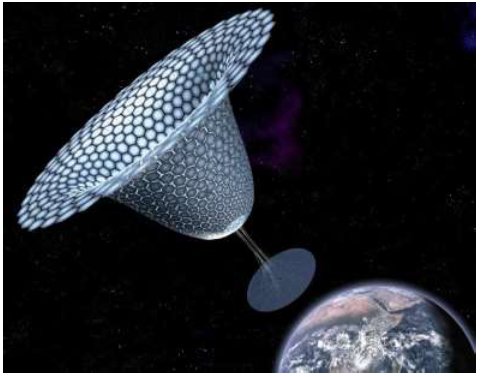
** Space based solar power has been failed to reach orbit despite decades of proposals and advocacy. Perhaps big drops in launch costs and cheaper SBSP system designs will finally make it practical, especially for powering remote sites: How to Get Solar Power on a Rainy Day? Beam It From Space | WIRED
In October, the Air Force Research Lab announced a $100 million program to develop hardware for a solar power satellite. It’s an important first step toward the first demonstration of space solar power in orbit, and [long time SBSP proponent John Mankins] says it could help solve what he sees as space solar power’s biggest problem: public perception. The technology has always seemed like a pie-in-the-sky idea, and the cost of setting up a solar array on Earth is plummeting. But space solar power has unique benefits, chief among them the availability of solar energy around the clock regardless of the weather or time of day.
It can also provide renewable energy to remote locations, such as forward operating bases for the military. And at a time when wildfires have forced the utility PG&E to kill power for thousands of California residents on multiple occasions, having a way to provide renewable energy through the clouds and smoke doesn’t seem like such a bad idea. (Ironically enough, PG&E entered a first-of-its-kind agreement to buy space solar power from a company called Solaren back in 2009; the system was supposed to start operating in 2016 but never came to fruition.)
See also
- SPS-ALPHA: The First Practical Solar Power Satellite – NASA
- SPS-ALPHA: The First Practical Solar Power Satellite via Arbitrarily Large Phased Array – 2011-2012 NASA NIAC Phase 1 Project – Final Report (pdf)
** Ntention‘s Astronaut Smart Glove tested at the Haughton Mars Project facility on remote Devon Island in northern Canada.
- Astronaut Smart Glove: Fashionable and Functional – Leonard David
- An Astronaut Smart Glove to Explore The Moon, Mars and Beyond | SETI Institute
The NASA Haughton-Mars Project (HMP) and collaborating organizations SETI Institute, Mars Institute, NASA Ames Research Center, Collins Aerospace, and Ntention are announcing the successful field test of an “astronaut smart glove” for future human exploration of the Moon, Mars, and beyond. The smart glove is a prototype for a human-machine interface (HuMI) that would allow astronauts to wirelessly operate a wide array of robotic assets, including drones, via simple single-hand gestures.
Here is a video about the project:
Haughton-Mars Project (HMP) video showing the first field test of a prototype “Astronaut Smart Glove”, a human-machine interface (HuMI) and augmented reality (AR) spacesuit system for future Moon and Mars exploration. Filmed at Haughton Crater, Devon Island, High Arctic. Collaborating organizations: Mars Institute, SETI Institute, NASA Ames Research Center, Collins Aerospace, and Ntention.
== Amazon Ad ==
The Case for Space:
How the Revolution in Spaceflight Opens Up
a Future of Limitless Possibility






